Fertilizer Production Line
Let’s Start Work
Together
Please feel free to contact us. We will get back to you with 1-2 business days. Or just call us now.
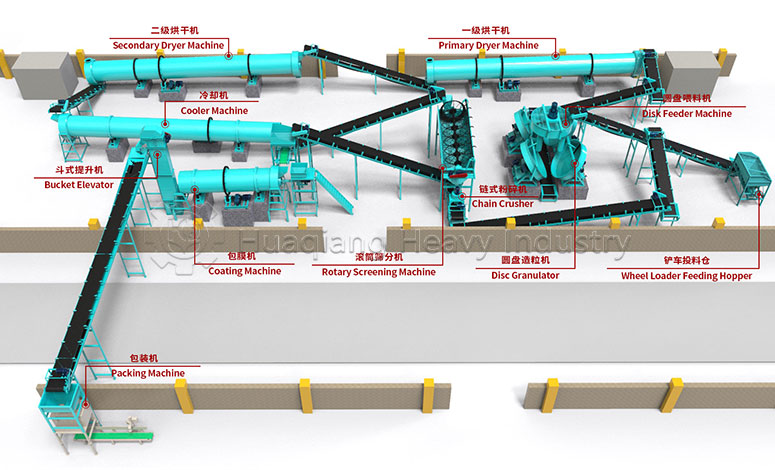
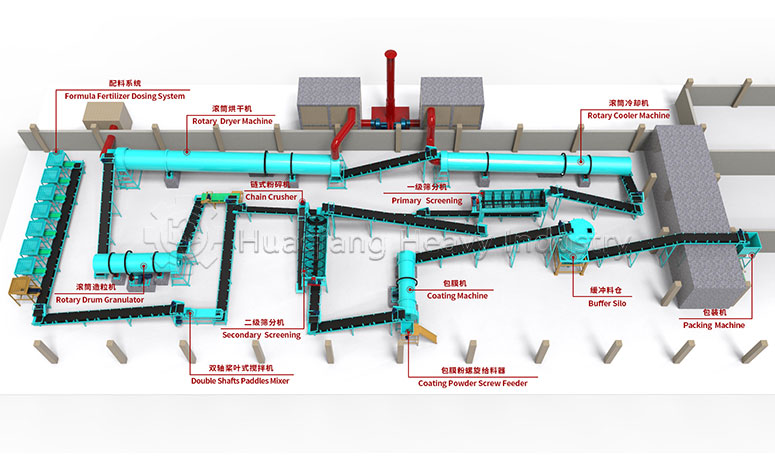
NPK Fertilizer Production Line
The NPK fertilizer production line is an automated production system specialized in producing compound fertilizers containing three main nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). The design of this production line aims to efficiently and accurately mix various raw materials, and through processes such as granulation, drying, cooling, and screening, produce NPK fertilizer granules with uniform particle size, stable nutritional content, and easy storage and use.
Equipment Composition
The NPK fertilizer production line typically includes the following key equipment:
Raw material processing equipment: including crushers and batching machines, used for crushing raw materials and accurately measuring the proportions of different components.
Mixing equipment: such as double axis blade mixer or V-shaped mixer, used to thoroughly mix the measured raw materials evenly.
Granulation equipment: such as disc granulators, drum granulators, or extrusion granulators, used to make granules from mixed materials.
Drying equipment: such as fluidized bed dryer or rotary drum dryer, used to remove moisture from particles after granulation.
Cooling equipment: such as a cooling drum, used to cool the dried particles to a suitable temperature.
Screening equipment: used to screen particles that are not qualified (too large or too small) to ensure consistent product particle size.
Coating equipment (optional): used to apply a thin film on the surface of fertilizer particles to improve moisture resistance and control nutrient release rate.
Packaging equipment: such as automatic packaging machines, used to weigh and package finished fertilizers.
Control system: including PLC control system and automation instruments, used to monitor and regulate the production process, ensuring the efficient operation of the production line.
Granulation process
1. Raw material preparation and pretreatment
Raw material measurement: Based on the target fertilizer formula, use measuring equipment to accurately weigh raw materials such as urea (N), phosphate (P), potassium salt (K), etc.
Raw material crushing: Send large pieces of raw materials into a crusher and crush them into particle sizes suitable for mixing.
2. Raw material mixing
Mixing: Feed the measured raw materials into a mixer, such as a double shaft blade mixer or a V-type mixer, and use mechanical force to thoroughly mix the raw materials evenly.
3. Granulation
Moisturizing with water: According to the granulation needs, add an appropriate amount of water to the mixture to achieve a suitable humidity for the raw materials, which is beneficial for granulation.
Granulation: Use a granulator, such as a disc granulator, drum granulator, or extrusion granulator, to make granules from the evenly mixed raw materials. The working principle of a granulator is usually to use rotation or pressure to form particles of a specific size and shape from the raw materials.
4. Drying
Drying: After granulation, the wet particles need to be sent to a drying machine, such as a fluidized bed dryer or a rotary drum dryer, to remove moisture from the particles through hot air or other drying media, preventing the particles from clumping during storage and transportation.
5. Cooling
Cooling: The dried particles have a high temperature and need to be cooled to a suitable temperature through cooling equipment, such as a cooling drum, to prevent the high temperature from affecting the fertilizer performance and facilitate subsequent processing and packaging.
6. Screening
Screening: After cooling, the particles are screened by a screening machine to select particles that meet the particle size requirements. Larger particles may need to be re granulated, while smaller particles may be treated as dust or reused.
7. Capsule (optional)
Coating: In order to improve the moisture resistance of fertilizers and control nutrient release rate, some production lines will apply coating treatment to qualified particles after screening, usually using a coating machine to coat a layer of organic or inorganic film on the surface of the particles.
8. Packaging
Automatic packaging: Finally, the finished fertilizer is weighed and packaged using an automatic packaging machine to form finished fertilizer bags, ready for storage or shipment.
9. Control and Monitoring
Automation control: The entire NPK fertilizer production line is usually equipped with advanced PLC control systems and automation instruments to monitor and adjust key parameters in the production process, such as raw material ratio, granulation humidity, drying temperature, etc., to ensure the stability of the production process and the quality of the product.
Process characteristics
- High degree of automation: The NPK fertilizer production line adopts an automated control system, which can achieve full automation production from raw material processing to finished product packaging.
- High production efficiency: Through optimized design and the use of efficient equipment, the production line can quickly and continuously produce a large amount of fertilizer.
- Product consistency: Through precise ingredients and granulation technology, ensure that the produced fertilizer particles maintain a high degree of consistency in size, shape, and nutritional composition.
- Flexibility: The production line can adjust the raw material ratio according to demand, produce NPK fertilizers with different formulas, and meet the needs of different crops and soils.
- Environmental protection and energy conservation: The design of production lines focuses on energy conservation and emission reduction. By optimizing processes and using energy-saving equipment, energy consumption and environmental pollution can be reduced. High degree of automation: The NPK fertilizer production line adopts an automated control system, which can achieve full automation production from raw material processing to finished product packaging. High production efficiency: Through optimized design and the use of efficient equipment, the production line can quickly and continuously produce a large amount of fertilizer. Product consistency: Through precise ingredients and granulation technology, ensure that the produced fertilizer particles maintain a high degree of consistency in size, shape, and nutritional composition. Flexibility: The production line can adjust the raw material ratio according to demand, produce NPK fertilizers with different formulas, and meet the needs of different crops and soils. Environmental protection and energy conservation: The design of production lines focuses on energy conservation and emission reduction. By optimizing processes and using energy-saving equipment, energy consumption and environmental pollution can be reduced.