Chicken manure is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but it is highly moist, sticky, and has a strong odor. Establishing a chicken manure organic fertilizer production plant requires focusing on the core principles of “harmlessness + resource utilization,” specifically addressing the challenges posed by the characteristics of the raw materials, balancing compliance, efficiency, and quality, and building a closed-loop production system.
Solidify the foundation of raw materials and site. Secure a stable source of chicken manure, sign long-term agreements with farms, and strictly control impurities in the raw materials. The site should be located far from residential areas and water sources, with reserved environmental protection distances. Different functional areas should be planned in zones, equipped with seepage-proof leachate collection ponds and odor treatment facilities to prevent secondary pollution.
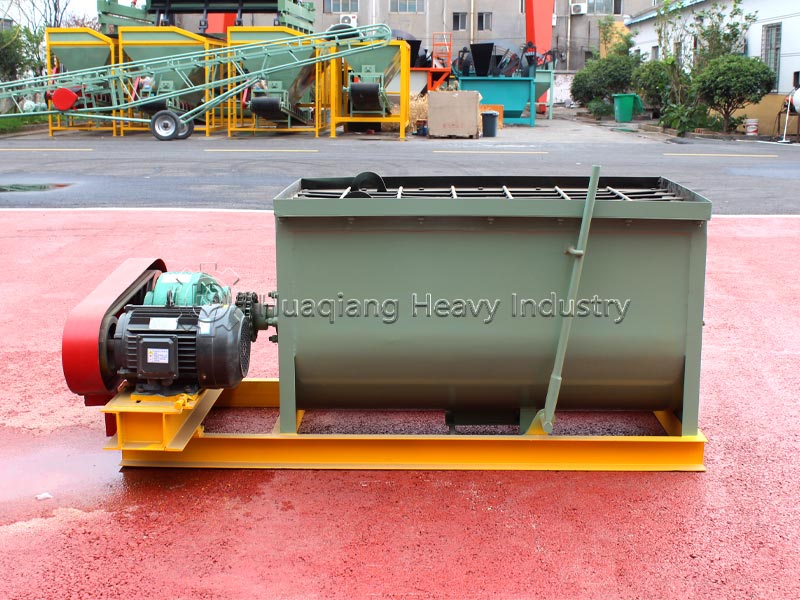
Set up the production line with suitable equipment. Equipment configuration based on scale: Pre-treatment uses a solid-liquid separator for dehumidification, paired with a fertilizer crusher and fertilizer mixer to mix chicken manure and straw/sawdust at approximately a 1:2 ratio to adjust the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio; fermentation uses horizontal fermentation tanks or double screws compost turning machines, maturing at 55-65℃ for 7-15 days for sterilization; deep processing includes granulation, screening, and packaging equipment to form a complete organic fertilizer production line.
Improve compliance and process systems. Obtain environmental protection filings, discharge permits, and finished fertilizer registration certificates, and establish a quality testing mechanism. Addressing the odor-prone nature of chicken manure, precisely control oxygen supply and turning frequency, and use microbial agents to accelerate maturation and reduce odor diffusion.
Build an operational closed loop. Control raw material costs and transportation losses, determine finished product types based on market demand, and connect with growers and agricultural input channels. Develop a regular equipment maintenance plan to ensure continuous operation of the production line.