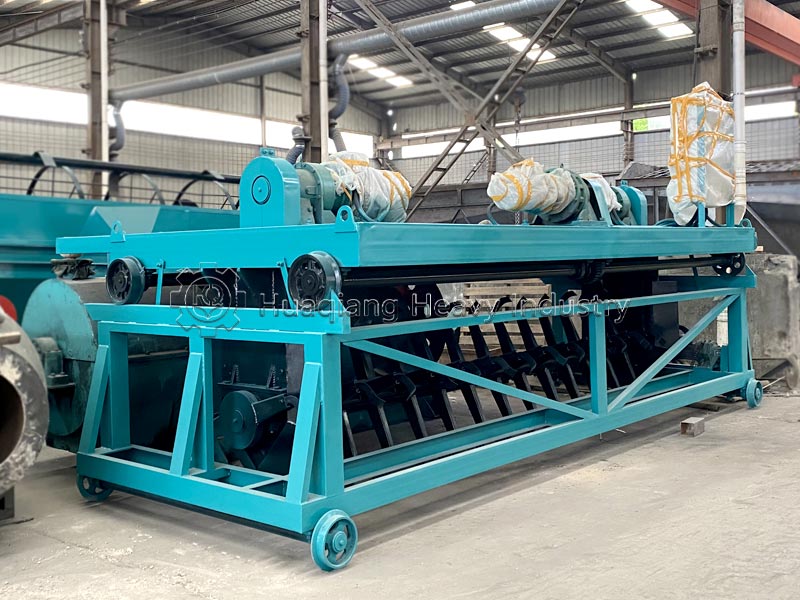
In organic fertilizer composting, rainwater runoff and leachate produced during material fermentation can easily cause secondary pollution and damage the composting environment if not treated properly. Rainwater can lead to excessive moisture in the compost pile, triggering anaerobic fermentation. Leachate contains high concentrations of pollutants, and direct discharge can pollute soil and water sources.
Rainwater treatment should focus on “prevention first, rapid drainage.” Composting sites should have a 1%-2% slope, equipped with drainage ditches and collection pits to prevent rainwater accumulation. For open-air composting, movable rain shelters should be built, covered with impermeable membranes during the rainy season, balancing rain protection and ventilation. Simultaneously, the composting area should be divided, and emergency drainage channels should be reserved. After rain, the compost should be turned over and the moisture dispersed using a compost turning machine.
Leachate treatment requires proper collection and harmless disposal. An impermeable membrane and collection pipes should be laid at the bottom of the composting area, flowing into a dedicated collection pool to prevent leakage and groundwater contamination. Small amounts of leachate can be reinjected into the compost pile, both to decompose pollutants with the help of microorganisms and to replenish the pile’s moisture. For larger quantities, after sedimentation and filtration pretreatment, the leachate can be treated biochemically or entrusted to professional organizations for disposal, ensuring it meets standards before discharge or reuse.
Treatment efficiency can be optimized by combining leachate with organic fertilizer composting equipment. For example, using a compost turning machine to control the pile’s porosity can reduce leachate production; adjusting the raw material ratio in advance during the rainy season, increasing the proportion of dry materials, can enhance water absorption capacity.
In summary, rainwater treatment focuses on “prevention and drainage,” while leachate treatment focuses on “collection and treatment.” The synergistic treatment of both can mitigate environmental risks and maintain the stability of the composting system, thus building a strong environmental protection barrier for organic fertilizer production lines.