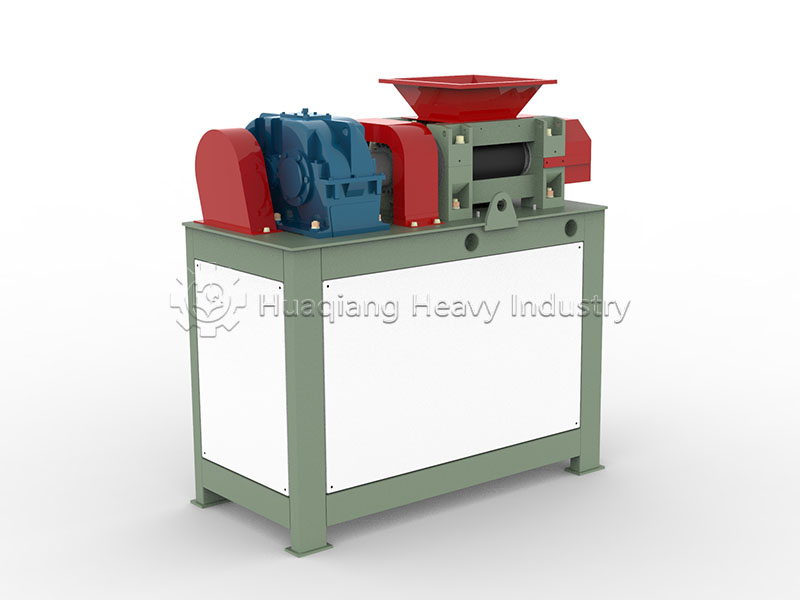
As a fiber-rich organic waste, the key to the resource utilization of oil palm empty fruit bunches lies in their forming and processing. Fertilizer compaction machines, with their targeted structural design, have become the core equipment for unlocking the granulation challenges of this type of fibrous raw material.
From the perspective of raw material compatibility, oil palm empty fruit bunches retain a large amount of tough fibers after fermentation and decomposition. This type of material has low viscosity and is prone to entanglement. Fertilizer compaction machines optimize the cooperation between the pressure rollers and the die holes, employing a large-area contact extrusion design. This allows the fibrous material to naturally unfold and pass through the die holes in the correct direction under pressure, avoiding entanglement and jamming.
Simultaneously, during the extrusion process, the fibers intertwine to form a “net-like support structure,” eliminating the need for excessive binders. Forming can be achieved solely through mechanical force and the material’s own viscosity, reducing production costs while ensuring the environmentally friendly properties of organic fertilizer.
The synergistic advantages of the two are particularly prominent in terms of forming effect and fertilizer retention. The low-temperature extrusion process of the fertilizer compaction machine minimizes the damage to organic matter and beneficial microorganisms in the oil palm empty fruit bunches caused by high temperatures, while preserving the loose fiber characteristics of the formed granules.
Furthermore, this synergistic approach optimizes the production process. The loose structure of the oil palm empty fruit bunches reduces frictional wear within the extruder, extending the lifespan of easily worn parts. Meanwhile, the fertilizer compaction machine’s high-efficiency forming capability rapidly transforms the decomposed oil palm empty fruit bunches into regular granules, solving the problems of dust generation during transport and uneven application of loose materials.