The core of efficient composting is ensuring microbial activity, which hinges on balancing the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, oxygen supply, and temperature. Choosing the appropriate composting method for different scenarios can significantly improve composting efficiency and product quality.
High-temperature aerobic static composting is the preferred method for large-scale production. The core principle is mixing raw materials at a ratio of 25:1-30:1, forming piles 1.5-2 meters high. The aerobic metabolism of microorganisms generates high temperatures of 55-65°C, killing pathogens and insect eggs. This method requires infrequent turning, has low costs, and is suitable for processing large quantities of livestock manure, straw, and other raw materials. The composting cycle is approximately 20-30 days, and the finished product has balanced nutrients, making it suitable for the basic fermentation needs of organic fertilizer production lines.
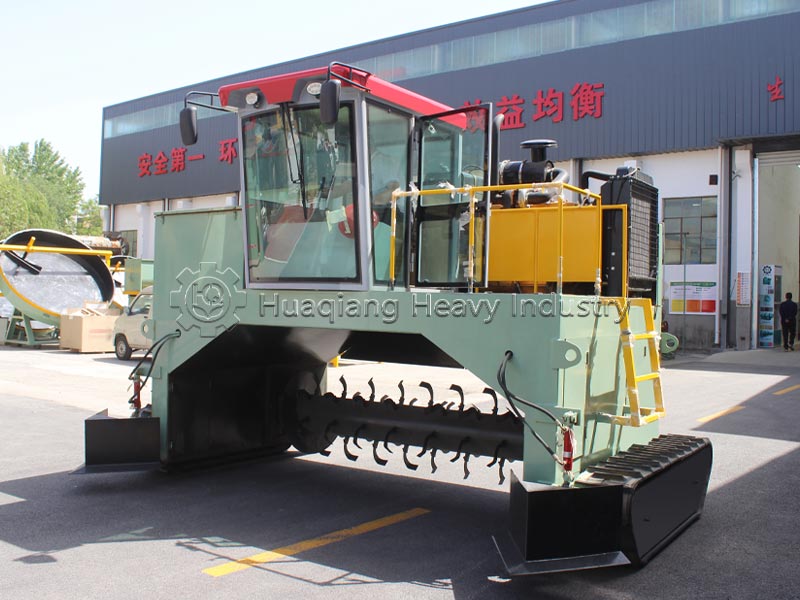
Windrow composting with turning is flexible and suitable for small and medium-scale scenarios. Raw materials are laid out in windrows 2-3 meters wide and about 1 meter high, and regularly turned with a crawler-type compost turning machine to maintain high-temperature fermentation. Its advantages include simple operation and low site requirements. The size of the windrows can be flexibly adjusted according to the amount of raw materials, and the turning frequency is dynamically adjusted based on temperature. The composting cycle is approximately 30-40 days, suitable for the decentralized composting needs of farms and individual farmers.
Closed-trough composting (such as using a double screws compost turning machine) is suitable for scenarios with high environmental requirements. A controlled environment is created through a closed box or trough, allowing for precise control of temperature, humidity, and oxygen supply, preventing odor leakage during the fermentation process. This method has extremely high composting efficiency, with a cycle of only 15-25 days. The finished product has high purity and effectively avoids secondary environmental pollution, making it suitable for refined composting scenarios with strict requirements for environmental protection and product quality.