Walking through the fields, few people consider how those nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium granules that nourish crops are actually manufactured. Their creation is not merely a chemical reaction, but an industrial journey of shaping form.
In modern fertilizer plants, production often begins with a series of precise physical mixtures. For blended fertilizers requiring flexible formulations, bulk blending fertilizer machines play a crucial role. Like a giant mixing bowl, it gathers bulk nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium raw materials from different sources according to a pre-set “recipe.” Amidst the roar of the machines, granules of various colors are efficiently and uniformly mixed, ensuring that every scoop of the final product contains a completely consistent nutrient ratio, laying the foundation for precision agriculture.
However, powder or physically mixed granules are sometimes not in the optimal form. To obtain fertilizers with higher strength and easier storage and application, fertilizer compaction machines demonstrate their power. Under powerful extrusion, they shape loose powder into uniformly sized, dense granules.
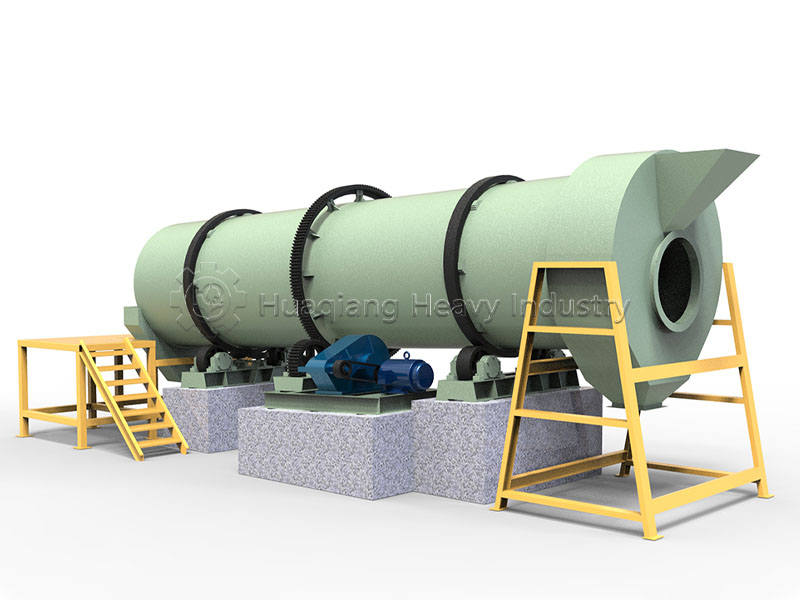
For large-scale continuous production, the rotary drum granulator paints a dynamic picture. Inside this slowly rotating giant cylinder, powdery raw materials are slightly moistened, tumbling, colliding, and agglomerating as the cylinder rotates, gradually growing into uniform, round granules.
From uniform mixing to powerful pressing and shaping, and then to rolling and agglomeration, the production of NPK fertilizer is a skillful shaping of nutrients by industrial forces. Ultimately, these granules of various shapes carry the same mission: to be integrated into the soil.